ZLD
Zero liquid discharge (ZLD) is an engineering approach to water treatment where all water is recovered and contaminants are reduced to solid waste. While many water treatment processes attempt to maximize recovery of freshwater and minimize waste, ZLD is the most demanding target since the cost and challenges of recovery increase as the wastewater gets more concentrated. Salinity, scaling compounds, and organics all increase in concentration, which adds costs associated with managing these increases. ZLD is achieved by stringing together water treatment technology that can treat wastewater as the contaminants are concentrated.

Concentrate your brine down to minimal liquid or even solid waste with our SaltMaker family of evaporative crystallizers. All are engineered as a complete MLD / ZLD package for corrosion and scale-free operation, automated self-cleaning, low cost site installation, and ease of service. We offer four classes of evaporative crystallizers:
- SaltMaker MultiEffect is a four-effect thermal evaporative crystallizer, with built- in heat recycle.
- SaltMaker AirBreather is a single effect thermal evaporator, with both open or closed to atmosphere options, suited for waste heat or low-cost heat sources .
- SaltMaker VapComp is a forced circulated mechanical vapor compression (MVR), suited for all-electric operation and delivered alongside our premier MVR partner
- SaltMaker ChilledCrys is a eutectic chilled crystallizer suited for specific ions pairs with a steep temperature-solubility curve such as sodium sulfate
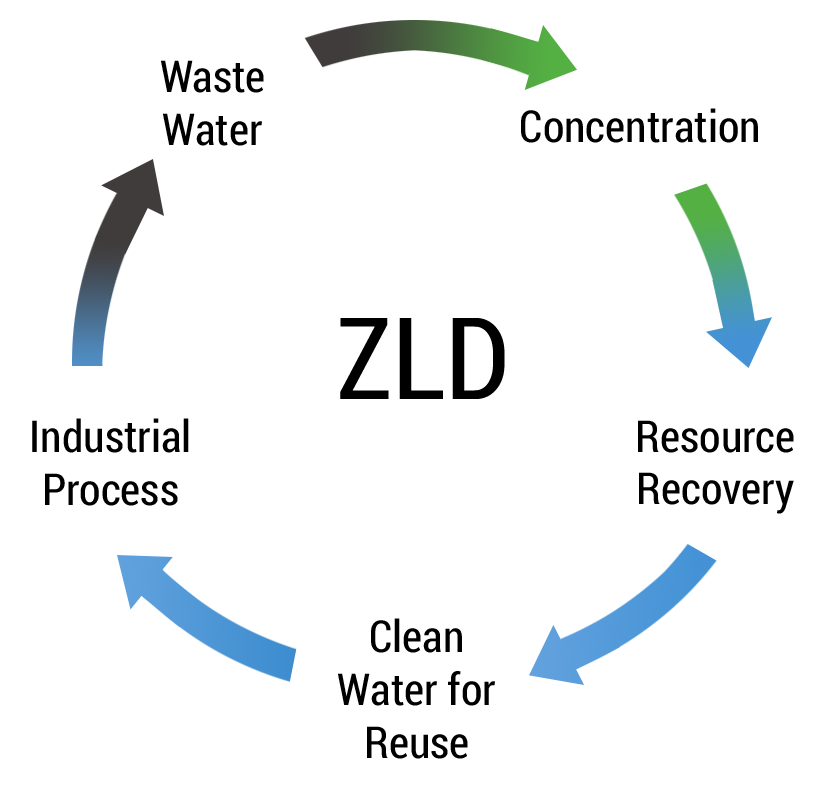
There are a number of benefits to targeting zero liquid discharge for an industrial process or facility:
- Lowered waste volumes decrease the cost associated with waste management.
- Recycle water on site, lowering water acquisition costs and risk. Recycling on-site can also result in less treatment needs, versus treating to meet stringent environmental discharge standards.
- Reduce trucks associated with off-site waste water disposal, and their associated greenhouse gas impact and community road incident risk.
- Improved environmental performance, and regulatory risk profile for future permitting.
- Some processes may recover valuable resources, for example ammonium sulfate fertilizer or sodium chloride salt for ice melting.
